Peer Reviewed
Feature Article Cardiovascular medicine
Atrial fibrillation: beyond drug therapies
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation is the most common, clinically relevant arrhythmia encountered in general practice with treatment options that continue to expand. This article provides a brief overview of the various types of atrial fibrillation and focuses predominantly on the currently available nonpharmacological treatment modalities.
Key Points
- Atrial fibrillation is the most common clinically relevant arrhythmia, which in most patients originates from abnormal ‘triggers’ within the pulmonary veins.
- Medical therapy and nonpharmacological approaches are often used together to treat symptoms of arrhythmia and prevent thromboembolic complications.
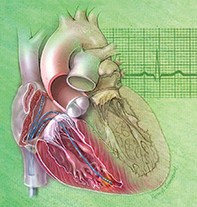
- Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation utilising a pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is a commonly used and highly effective procedure to treat symptomatic patients, especially if used early.
- An ablation of the atrioventricular node and a pacemaker insertion can be useful in improving symptoms in patients who remain symptomatic despite all other treatment attempts.
- Left atrial appendage occlusion devices can be effective in reducing thromboembolic complications if anticoagulation is contraindicated.
Picture credit: © Kevin A. Somerville.
Purchase the PDF version of this article
Already a subscriber? Login here.