Peer Reviewed
ECG education
Left bundle branch block
Abstract
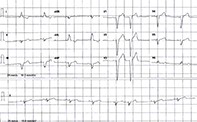
An ECG of a healthy young man shows a left bundle branch block. What are the potential causes and significance of this ECG pattern?
Key Points
- Generally, in patients with LBBB, the QRS complex is more than 120 msec in duration with upright monomorphic R waves in V5, V6, aVL and lead I without Q waves. There is no secondary R wave inV1.
- Incomplete LBBB is diagnosed when a patient has the ECG criteria for LBBB but the QRS duration is less than 120 msec.
- It is difficult to be definite of an acute myocardial infarction in the presence of an LBBB without a rise in the serum troponin level and/or classic symptoms and signs.
- Patients with incomplete or complete LBBB require full investigation, including a cardiac echocardiography, assessment of cardiovascular risk factors, consideration of functional stress testing and a cardiology consultation.
- Patients with no impairment of exercise tolerance and no evidence of cardiac failure do not require any treatment other than reducing their cardiovascular risk factors as appropriate.
- Pacemaker cardiac resynchronisation therapy is required for patients with LBBB who have a reduced ejection fraction, those who are symptomatic with exertion and those who have cardiomyopathy.
Purchase the PDF version of this article
Already a subscriber? Login here.